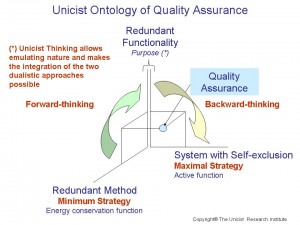
 The Unicist Standard provides the fundamentals to define and implement reliable Quality Assurance systems.
The Unicist Standard provides the fundamentals to define and implement reliable Quality Assurance systems.
Quality assurance is a characteristic that systems have, whether they include human action or not, to provide an accurate result to the point of being substituted by alternative systems in case of failure.
Nothing is absolutely certain by definition within the scope of science. When we refer to certainty we mean that there are at least three alternative plans in case of failure and that alternative processes have been designed to have a probability of failure of less than 0,01.
In order to assure this level of certainty it is necessary to count on a verification process in real conditions that ensure the result or output.
Elements included in a Quality Assurance System:
1) Plan “B”
2) Redundant Systems
3) Alarm System
4) Processes with redundancies
5) Stop System (stoppage/halt)
6) Control System
7) Self repairing/recovery System
8) Alternative Systems
The first step to achieve reliability is having an adequate quality assurance system.
